Eating fried eggs can cause heart disease and cancer, experts warn.
Prolonged temperatures above 350F can cause the release of chemicals associated with inflammation and thickening of the arteries.
These chemicals, called oxysterols, are produced when dietary cholesterol is cooked at high temperatures for long periods of time.
This means that hard-fried eggs may be at risk of developing these chemicals, which are linked to heart disease and cancer, according to Angel Luk, a Canadian nutritionist.
Instead, he recommends choosing omelets and other eggs that cook best at low temperatures.
And limit the oil, because too much can cause the eggs to overcook.
In addition to heart disease, oxysterols have also been linked to other types of cancer such as colorectal and bladder cancer.

Hard-boiled eggs can release harmful chemicals called oxysterols, which have been shown to increase the risk of heart disease and several cancers (stock photo).
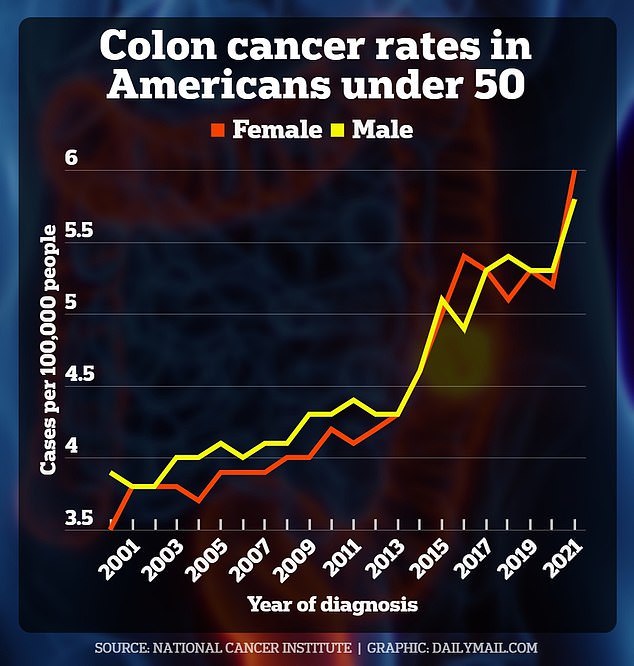
The graph above shows the rise in colorectal cancer in Americans under 50 over the past two decades
However, eggs are a nutritious food that has been shown to help with weight loss, muscle strength, and heart health due to their high levels of protein, amino acids, and brain nutrients like choline.
They are also rich in HDL cholesterol, the “good” cholesterol that helps remove excess fat from the body and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Research on oxysterols in eggs has also been limited compared to the evidence on the benefits of breakfast.
Ms Luk told Health Digest that when HDL cholesterol is burned, ‘chemicals called oxysterols can be produced.
‘Some research shows that oxysterols have negative effects on health, including increasing the risk of heart disease and cancer.’
According to a 2019 study from the National Institutes of Health, oxysterols can increase oxidative stress, where unstable molecules called free radicals damage cells and tissues and cause inflammation.
This oxidative stress destroys disease-fighting antioxidants, leaving the body defenseless against cancer cells.
A 2018 review showed that oxysterols increase the risk of breast, prostate, colon, and bile cancer.
And a study published last month in the journal Cancer Prevention Research found that high levels of oxysterol increased the risk of colon cancer by 22 percent.
Additionally, a 2017 study in Lipids in Health and Disease found that oxysterols bind to LDL, or ‘bad’ cholesterol, which causes harmful plaque to build up in the arteries.
This makes it difficult for blood to flow properly in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Cooking eggs at high temperatures, such as 350 degrees Fahrenheit (176 degrees Celsius), often causes oxysterols to form, research has shown.
Hard-boiled eggs, which are usually fried longer than other types such as over-easy, are considered cooked after five minutes at high heat.
Processed meats such as sausages cooked at high temperatures have also been shown to release oxysterols.
To reduce the risk of producing oxysterols, Ms Luk recommended choosing eggs that can be cooked at low temperatures, such as scrambled eggs and omelets.
She said: ‘I recommend making a veggie omelet with a little oil that is not heated, without cooking the eggs.
‘In this way, the protein in the egg is easily digested while the vegetables provide additional nutrients and antioxidants.’
He also said to use avocado oil, because it has a lot of monounsaturated fat that lowers cholesterol, reduces the risk of heart disease.
#cook #eggs #unexpected #effect #CANCER #risk